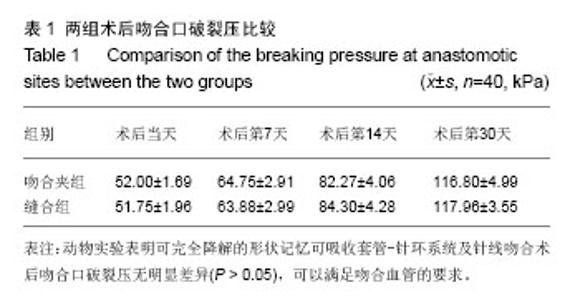
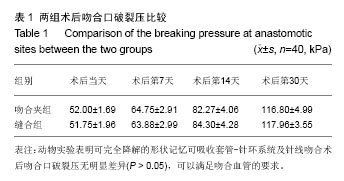
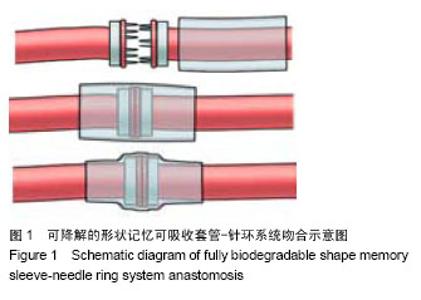
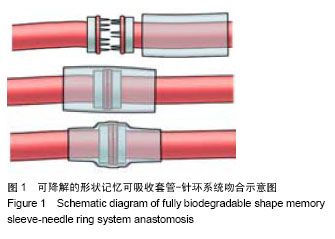
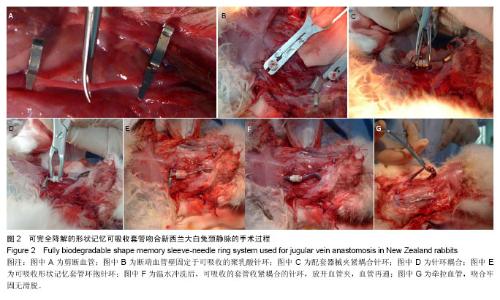
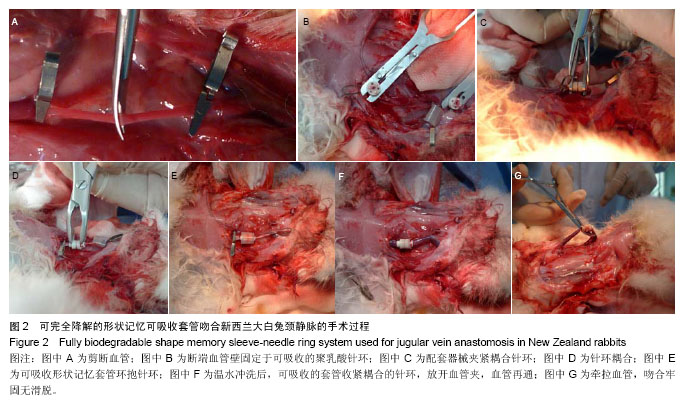
| [1] Holt GP, Lewis FJ.A new technique for end-to-end anastomosis of small arteries.Surg Forum. 1960;11:242-243.
[2] Nakayama K, Tamiya T, Yamamoto K,et al.A simple new apparatus for small vessel anastomosisi (free autograft of the sigmoid included).Surgery. 1962;52:918-931.
[3] Ostrup LT, Berggren A.The UNILINK instrument system for fast and safe microvascular anastomosis.Ann Plast Surg. 1986;17(6):521-525.
[4] Sullivan SK, Dellacroce F, Allen R.Management of significant venous discrepancy with microvascular venous coupler.J Reconstr Microsurg. 2003;19(6):377-380.
[5] Yap LH, Constantinides J, Butler CE.Venous thrombosis in coupled versus sutured microvascular anastomoses.Ann Plast Surg. 2006;57(6):666-669.
[6] Spector JA, Draper LB, Levine JP,et al.Routine use of microvascular coupling device for arterial anastomosis in breast reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 2006;56(4):365-368.
[7] Hallock GG, Rice DC.Early experience with the new 'megacoupler' ring-pins for microvascular anastomoses.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61(8):974-976.
[8] Hallock GG, Rice DC.Use of a microvascular coupler for repair of major distal upper extremity artery injuries.J Hand Microsurg. 2009;1(1):3-6.
[9] 刘英炳,陈受谦,杨恒文,等.73-2型血管吻合器的动物实验和临床应用[J].解放军医学杂志,1979,4(2):76-80.
[10] 林民专,赵明,高伟,等.应用钛环血管吻合器建立大鼠原位肝移植模型[J].中华器官移植杂志,2000,21(6):339-340.
[11] 王守界,宋建新,邢新,等.血流动力学定量指标评估微型钛血管吻合夹吻合静脉的实验研究[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(2):74-75.
[12] 刘延.使用钛轮钉与手工吻合在建立动静脉内瘘上的比较[J].第四军医大学学报,2007,28(22):2043.
[13] 王俊峰,谢席胜,周红梅,等.血液透析患者两种动静脉内瘘成形术的比较[J].西部医药,2008,20(5):1007-1009.
[14] 刘春,王倩,周泽梅,等.建立动静脉内瘘直接缝合法与钛轮钉吻合法的对比研究[J].重庆医药,2008,37(10):1081-1082.
[15] 徐政全,陶建萍.血液透析患者动静脉内瘘闭塞原因分析及预防措施[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2008,17(5):571-752.
[16] 严红霞.头静脉-桡动脉内瘘闭塞的原因及预防措施[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2008,29(19):2344.
[17] 王云生,胡祥仁,吴孟华,等.钛轮钉血管吻合术在长期血液透析病人中的应用[J].西南国防医药,2007,17(3):316-317.
[18] 罗庚,郭现辉,江宏,等.钛轮钉在动静脉内瘘中的应用[J].中原医刊,2004,33(8):25-27.
[19] 周峰,叶钢.应用钛轮钉机械吻合对比手工吻合肾移植动脉的临床研究[J].重庆医科大学学报,2009,34(9):1207-1209.
[20] 陈扬波,杨忠明,杨庆雄,等.应用血管吻合器治疗四肢血管伤的体会[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(3):267.
[21] 戚悠飞,朱晒红,王国慧,等. 聚L-乳酸血管吻合套管的初步研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2012,22(16):9-14.
[22] 许硕贵,朱光明,张春才.一种生物可吸收捆绑带及其形状记忆锁扣:中国,200610023175[P].2006-08-23.
[23] 朱光明,许硕贵,费敬银,等. 辐射交联聚己内酯的非等温结晶动力学研究[J].辐射研究与辐射工艺学报,2004,22(6):349-355.
[24] 朱光明,秦瑞丰,许硕贵.具有电响应特性的形状记忆材料及其制备方法: 中国,200410073393[P].2005-07-13.
[25] 沈岳,钟孝正,龙在云,等.生物降解桥接套管修复显微血管的实验研究[J].中国现代医生,2008,46(24):1-2.
[26] 范恒华,伍骥.血管粘接吻合密封胶(剂)的实验研究[J].医疗卫生设备,2009,30(10):1-4,7.
[27] 梁向党,张伯勋,孙赓,等.微创血管粘合技术研究的初步报告[J].医疗卫生设备,2005,26(7):23-25.
[28] 刘鲁伟,杨继庆,王斯刚,等.激光血管环形吻合仪的研制[J].现代电子技术,2005,28(13):89-90.
[29] 查选平,宋建星,邢新,等. 微型钛血管吻合夹吻合血管的生物力学研究[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(16):2388-2389.
|